Many Master Bond epoxy systems are formulated with superior chemical resistance. We continually test our materials by exposing them to specific chemicals over a long period of time. A common way of testing the chemical compatibility of an epoxy is immersing a sample in a chemical and measuring its change in weight over time. A significant loss or gain in weight would indicate a decreased ability of a material to stand up to chemical exposure. These tests allow us to more accurately recommend the right product based on specific application requirements.
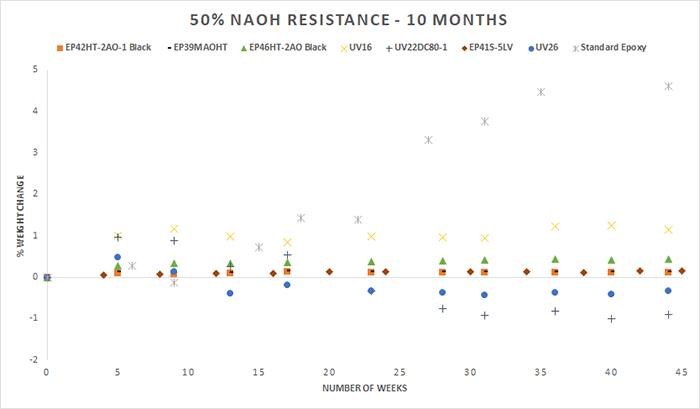
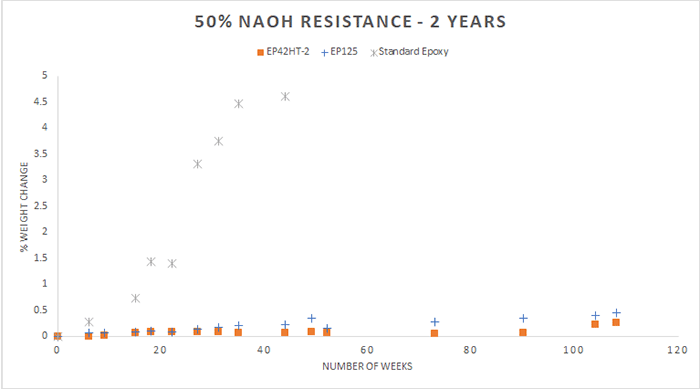
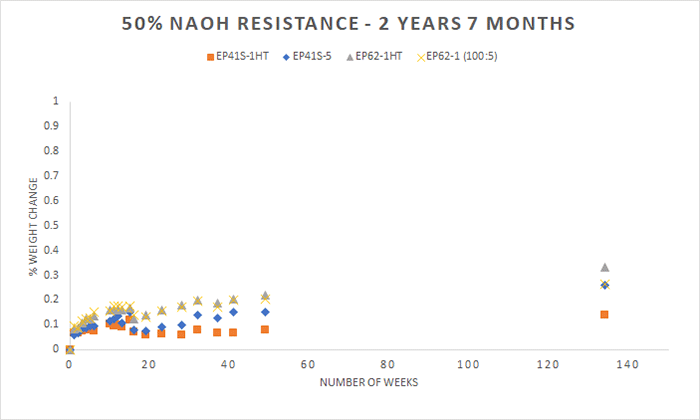
In this experiment, we focused on testing our epoxies for their resistance to 50% sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The compounds Master Bond used for testing are a variety of two component epoxies and one component UV curing systems with good overall chemical resistance. For the first round of testing, which involved exposure to 50% NaOH for 10 months, the products tested were EP42HT-2AO-1 Black, EP39MAOHT, EP46HT-2AO Black, UV16, UV22DC80-1, EP41S-5LV and UV26. For the second round of testing, which involved exposure to NaOH for two years, the products tested were EP42HT-2 and EP125. For the third round of testing, which involved exposure to NaOH for more than two and a half years, the products tested were EP41S-1HT, EP41S-5, EP62-1HT, and EP62-1 (with a 100:5 mix ratio).
A few thin castings, roughly 2 inches in diameter and around 0.125 inches thick, were made for each product and cured in accordance with their specifications. Once the cured samples were created and initial weight was recorded, the castings were immersed in 50% NaOH. Then, we continued recording frequent weight measurements. Below you will see the results of soaking for these various time intervals. The castings were weighed periodically, and the graphs shown below demonstrate the percentage of weight change over time.
Testing Adhesives for Resistance to NaOH
For the purpose of comparison, please note that for the ten month and two-year exposures, a casting of a standard epoxy was also tested under these same conditions which served as a reference. As can be seen in the graphs, the standard epoxy was markedly less resistant to 50% NaOH than the other epoxies tested, although it performed well for about the first 10 months. It demonstrated a significantly greater change in weight over time and the casting ultimately dissolved in 50% NaOH after approximately one year.
Chemicals can etch the surface of an epoxy (resulting in weight loss) or they can cause swelling of the sample (resulting in weight gain). In general, a weight change of less than 4-5% (gain or loss) can be considered excellent, especially since these tests may be more rigorous compared to actual service conditions. It is also worth noting that in the context of a bonded joint or a potted assembly the exposure to 50% NaOH might not be as severe or direct as in the above test conditions.
Please note, when choosing an epoxy for an application where the resistance to 50% NaOH is critical, many other factors must be considered in addition to the chemical resistance. Nearly all the products tested performed well, even with prolonged exposure to 50% NaOH. However, depending on the time of exposure to 50% NaOH, each of the epoxies in the charts above offers a distinct set of performance properties. If low shrinkage and dimensional stability are needed, EP39MAOHT can be considered. For longer term exposures, if a high glass transition temperature is needed, EP62-1HT is a good choice. EP41S-5 may be considered if electrical insulation and low outgassing are the priorities. These products all need to be processed or cured differently but the key in all cases is the addition of heat for enhancing/optimizing chemical resistance especially to 50% NaOH.
Disclaimer: The findings in this article are not meant to be used for specification purposes.
Master Bond Acid Resistant Epoxies
 |
EP62-1HT Superior resistance to harsh chemicals, particularly to acids. Two part epoxy has long pot life at ambient temperatures. High bond strength properties. Ideal for bonding and coating. Good flow. Reliable electrical insulator. Serviceable from -60°F to +450°F. Tg 150-160°C. Shore D hardness 80-90. |
 |
EP41S-5LV Excellent chemical resistance to solvents, alcohols, fuels, acids and bases. Low viscosity with good flow properties. Can be used for potting/encapsulation. Formidable physical strength properties. Serviceable from -80°F to +350°F. |
 |
EP39MAOHT Thermally conductive, low viscosity potting/encapsulation compound. Superior dielectric properties. Versatile cure schedules. Convenient one to one mix ratio weight or volume. Minimal shrinkage and stress development. Resists thermal cycling and mechanical shocks. Service temperature range -100°F to +400°F. |
 |
EP125 Structural epoxy adhesive resists temperatures up to 500°F. Exceptional durability and flexural strength. High adhesion to metallic and non-metallic substrates. Heat curable system. Tg +240°C. Special two part epoxy with very long working life. Excellent compressive strength. Service operating temperature range from -80°F to +600°F. |
 |
EP42HT-2AO-1 Black Good heat conduction. Serviceable from 4K to +400°F. Resists water, oils, fuels. Excellent dielectric properties. Enhanced dimensional stability. Castable up to 2-3 inches thick. Low shrinkage upon cure. Good flow. Meets NASA low outgassing standards. |
 |
UV26 Specialty type UV curable adhesive with very fast curing time and high thermal stability. Its glass transition temperature is 160 to 170°C and its service temperature range is -60°F to +500°F. UV26 resists acids, bases, fuels, and many aggressive solvents. |
